The Importance of Emotions and AI's Role
In the complex tapestry of human interaction, emotions play a leading role. They are the compass guiding our decisions, coloring our perceptions, and shaping our relationships. Correctly recognizing and interpreting the moods of others is an intrinsically human ability, fundamental for empathy and effective communication. But what if machines could also develop such sensitivity? AI is opening previously unimaginable frontiers in this field.
Decoding Dynamic Facial Expressions
The human face is an incredibly rich expressive canvas. The subtlest muscle contractions, the tilt of the eyebrows, the curve of the lips: every detail can convey valuable information about a person's emotional state. AI is proving particularly adept at analyzing these micro-expressions, going beyond the simple interpretation of static images. Advanced technologies can now process video sequences, capturing the dynamics of emotional expression as it evolves over time.
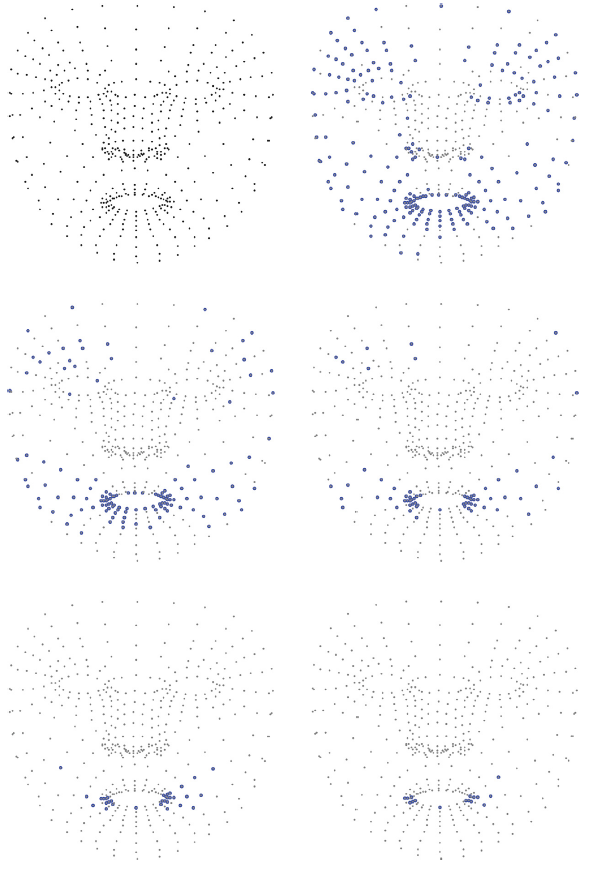
The Facial Landmark Approach
An innovative approach relies on identifying and tracking hundreds of "landmarks" on the face. Imagine an incredibly detailed digital map of the face, composed of nearly 500 key points. By monitoring the precise coordinates of these points and their variation from one frame to the next, AI algorithms can reconstruct the emotional flow with remarkable accuracy, distinguishing between states like joy, sadness, surprise, anger, fear, or disgust. This method allows capturing not only the peak emotion but also the transition from a neutral state to the full expression.
Balancing Accuracy and Speed with Randomization
But how can these analyses be made not only accurate but also fast and efficient, especially for applications requiring real-time responses? This is where a fascinating concept comes into play: "randomized" neural networks. Instead of meticulously training every single parameter of the neural network, a process that can require significant time and computational resources, some parts of the network are set with random values and then "frozen." This approach, while potentially involving a very slight reduction in theoretical accuracy, drastically speeds up the learning phase and the algorithm's execution. It's a smart trade-off between accuracy and speed, crucial for bringing these technologies into the real world, onto devices with limited capabilities, or in scenarios where latency is critical.
Transformative Real-World Applications
The potential applications of AI capable of "reading" emotions are vast and transformative. Consider the healthcare sector: systems capable of monitoring subtle changes in facial expressions could aid in the early diagnosis of conditions like depression or chronic stress, supporting doctors and patients. Imagine e-learning systems that adapt educational materials based on the student's emotional reaction, making learning more personalized and effective. Or even more intuitive and empathetic human-machine interfaces, capable of responding more appropriately to our moods, enhancing user experience in countless contexts, from recommendation systems to road safety.
Towards Emotionally Aware Technology
The integration of AI into emotion recognition is not science fiction. By leveraging detailed facial landmark analysis and the efficiency of randomized networks, we are building systems increasingly capable of understanding the complex language of human emotions. This opens doors to a future where technology is not only functional but also more aware and attuned to our emotional experiences, promising significant improvements in crucial areas like health, education, and daily interaction.